You have dozens of online accounts, each needing a strong, unique password. Remembering them all?
Nearly impossible. That’s where tools like password managers and password vaults come in—but are they the same? Or do they serve different purposes? Understanding the difference between a password manager and a password vault can make a big impact on how secure and organized your digital life truly is.
If you want to protect your sensitive information without getting overwhelmed, keep reading—because knowing which tool fits your needs can save you from frustration and risk.

Table of Contents
TogglePassword Manager Basics
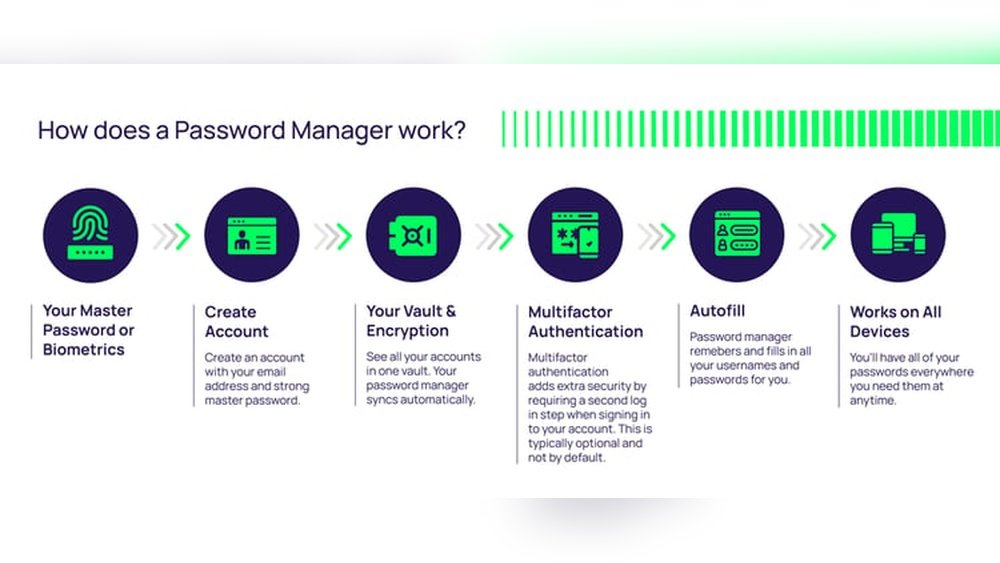
A password manager is a tool designed to store and organize your passwords securely. It helps you create strong and unique passwords for every account. You only need to remember one master password to access all your saved logins. This makes managing passwords easier and safer.
Password managers often include a password vault. The vault is the secure, encrypted space where your data is stored. The manager is the application that organizes and fills in your passwords when needed. Understanding these basics helps you choose the right tool to protect your online accounts.
Core Features
Password managers offer encrypted storage for passwords and personal data. They generate strong passwords to improve security. Autofill options quickly enter your login details on websites. Syncing across devices keeps your information accessible everywhere. Many also alert you to weak or reused passwords.
How It Works
You create one master password to unlock the manager. The app stores all other passwords inside a secure vault. When you visit a site, the manager fills in your login automatically. It encrypts your data, protecting it from hackers. Backup and recovery options keep your passwords safe if you lose access.
Common Uses
People use password managers to handle many online accounts easily. Businesses use them to share passwords securely among employees. They help avoid using the same password on multiple sites. Password managers also reduce the risk of forgotten passwords. They simplify logging in on phones, tablets, and computers.
Password Vault Essentials
A password vault is a secure digital container. It holds your passwords and sensitive data safely. This section explains the key features of a password vault. Understanding these helps you choose the right tool for your needs.
Using a vault keeps your information protected and easy to manage. Here is what makes a password vault essential for security.
Secure Storage Explained
Password vaults use secure storage to keep your data safe. They lock your information inside a protected space. This storage prevents hackers from accessing your passwords. Only you can open this vault with a master password.
Your sensitive data like login details and credit card numbers stay protected. The vault acts like a digital safe, guarding your private information.
Encryption And Access
Encryption is the core of password vault security. It turns your data into unreadable code. Only your master password can decode this information. This process keeps your passwords hidden from others.
Access to the vault requires strong authentication. You must enter your master password to unlock it. Some vaults also use extra steps like two-factor authentication for more safety.
Organizing Credentials
Password vaults help you organize your credentials easily. You can group passwords by categories or tags. This makes finding login details quick and simple. Proper organization reduces confusion and saves time.
Many vaults allow notes and attachments for each entry. This feature helps you keep related information together. A well-organized vault improves your password management experience.
Key Differences
Understanding the key differences between a password manager and a password vault helps you choose the right tool. Both aim to protect your sensitive information but serve slightly different roles. Knowing these differences improves your digital security and ease of use.
Functionality Comparison
A password manager stores and organizes your passwords for easy access. It also helps autofill login details on websites and apps. A password vault mainly focuses on secure storage of passwords and sensitive data. It acts like a locked safe where all your secrets are kept. Managers include vaults, but vaults do not manage passwords actively.
User Experience
Password managers offer a smooth and simple experience. They automatically fill in passwords and suggest strong ones. This saves time and reduces login errors. Password vaults require manual access and retrieval of stored data. They offer less automation but strong control over stored information. Managers are generally more user-friendly for daily use.
Security Levels
Both use strong encryption to protect your data from hackers. Password vaults focus entirely on secure storage with advanced encryption methods. Password managers balance security and convenience, encrypting data while enabling autofill features. Master passwords unlock both, so choosing a strong master password is vital. Some managers add extra security layers like two-factor authentication.
Benefits Of Each
Understanding the benefits of password managers and password vaults helps you choose the right tool. Both improve your online security by protecting sensitive data. Each has unique strengths that fit different needs and preferences. Knowing these advantages makes managing passwords easier and safer.
Advantages Of Password Managers
Password managers save and organize passwords automatically. They fill in login details on websites quickly. This saves time and reduces typing errors. They generate strong, unique passwords for each account. This lowers the risk of hacking. Password managers sync across devices for easy access. They alert you about weak or reused passwords. Many offer extra features like two-factor authentication support. User-friendly interfaces make them easy to use for beginners.
Strengths Of Password Vaults
Password vaults focus on storing data in a highly secure space. They use strong encryption to protect your information. Vaults keep passwords, credit cards, and notes in one place. Access requires a master password or biometric login. Vaults often work offline, reducing exposure to online threats. Some vaults allow sharing access safely with trusted people. They provide a centralized place to manage all sensitive data. Vaults can offer extra security layers, like security questions or time locks.
Potential Weaknesses
Both password managers and password vaults offer strong protection for your sensitive data. Yet, they have some weaknesses you should know. Understanding these can help you use them more safely and wisely.
Common Vulnerabilities
Many password managers and vaults rely on one master password. If this password is weak or stolen, all stored data is at risk. Hackers may try to guess or steal this password. Some tools lack multi-factor authentication, which adds an extra security layer.
Software bugs and security flaws can also expose your data. Attackers may exploit these weaknesses to access your vault. Regular updates and security patches are crucial to reduce these risks. Not all users keep their software updated, which can be dangerous.
Limitations On Compromised Devices
If your device is infected with malware, password managers and vaults offer limited protection. Keyloggers can capture your master password as you type it. Screen capture malware may record your screen when you access passwords.
Some password tools do not detect or block such threats. This makes your data vulnerable even if stored securely. Avoid using password managers on devices that may be compromised. Use trusted devices and keep security software active to protect your data better.
Use Cases And Recommendations
Understanding the use cases and recommendations for password managers and password vaults helps you pick the right tool. Both keep your sensitive data safe, but their focus and features differ. Knowing their strengths supports better security choices for different needs.
Best For Personal Use
Password managers suit individuals who want simple, secure login storage. They store passwords, autofill forms, and generate strong passwords easily. Most personal users benefit from apps with user-friendly interfaces and cross-device syncing. These tools help avoid weak or repeated passwords, improving online safety.
Ideal For Enterprises
Password vaults fit businesses that need centralized control over many users. They offer encrypted storage with strict access rules and audit logs. Companies use vaults to manage employee credentials and sensitive data securely. Vaults support compliance with security standards and reduce risks from insider threats.
Choosing Based On Needs
Decide based on who will use the tool and what information it will protect. Personal users gain from password managers’ ease and automation. Businesses require vaults for stronger access controls and team management. Evaluate your security goals, budget, and technical skills before selecting one.
Future Trends
The future of password management holds many exciting changes. Both password managers and password vaults will evolve to become more secure and user-friendly. These tools will adapt to new threats and technologies. Users will benefit from smarter, safer, and faster password solutions.
Advancements In Security
Password managers and vaults will use stronger encryption methods. Biometric authentication will become more common. Fingerprint and facial recognition will add extra layers of protection. Continuous monitoring will detect unusual login attempts instantly. This will reduce the risk of hacking and data theft.
Integration With Other Tools
Password tools will connect better with other apps and devices. They will work seamlessly with browsers, email, and cloud services. Single sign-on (SSO) features will become more popular. Users will manage passwords alongside identity and access controls. This will simplify security across multiple platforms.
Emerging Technologies
Artificial intelligence will help generate and manage passwords. AI will spot weak passwords and suggest stronger ones. Machine learning will identify suspicious activities early. Blockchain technology may offer new ways to secure password data. These innovations will improve trust and ease of use.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Difference Between Password Manager And Vault?
A password manager is an app that organizes and autofills passwords. A vault is the encrypted storage space within it. The manager handles your data, while the vault securely stores it. Both work together to protect and manage your login credentials safely.
Are Password Vaults A Good Idea?
Password vaults securely store and encrypt your passwords, making it easy to use strong, unique credentials. They enhance online security and simplify login management.
Why Don’t Older Adults Use Password Managers?
Older adults often avoid password managers due to limited tech skills, fear of complexity, and concerns about security risks.
Is Vault A Password Manager?
Yes, Vault is a password manager that securely stores and organizes your login credentials in an encrypted digital vault.
Conclusion
Choosing between a password manager and a password vault depends on your needs. Both keep your information safe and organized. Password managers help autofill and manage passwords easily. Password vaults focus on securely storing your data in one place. Using either tool improves online security and reduces password stress.
Remember to pick a trusted option and use a strong master password. Stay safe by keeping your digital life protected and simple.
This post contains affiliate links. I may earn a commission if you make a purchase through them, at no extra cost to you.